English Architecture

Villas usually homed the owner and his family, as well as his labourers and overseers. In addition, it included storehouses and any other buildings required to further the work of the householder.
At first, most of the Roman buildings were constructed out of wood, using either wood or stone for the foundations. Then, during the following century, they were rebuilt from sturdier stone, making them more resilient to fire and the climate.??
The styles of each building were very different, but they were characterised by being a single story with roofs tiled in slate or clay tiles. Many had marble, mosaic or tiled floors; plastered walls that had been painted; central heating and even heated floors. The most popular time for Roman villas was during the 100.s and 200.s EC.
Anglo-Saxon
Because the Anglo-Saxon period was one of much violence and war, many of the original buildings of this time were destroyed. In fact, the Vikings of the ninth and 10th centuries would literally plunder entire settlements, looting and destroying them. However, there are a few examples of this era that still survive.
This era was one during which wood with wattle and daub (clay mixed with straw) was used to construct the walls. Stone was generally only used for monasteries and churches, which means that these buildings are the most likely to have survived the centuries. Most Anglo-Saxon remains of these stone buildings can be found in the areas of Kent (e.g. Canterbury and St. Peter) and Northumbria (at Tyne and Wear and Escomb).
Let us consider what the advantages and disadvantages of Phone Repairs.
Most of the remaining churches from this period are small (as the larger ones were rebuilt in the Norman style), with simple layouts and limited ornamental features. Windows were usually narrow with rounded tops. Towers were of particular importance during this time, originally intended for the defence and protection of the town. Another common characteristic was that of long lines of vertically-oriented stones on the outside walls.
The Saxon-style homes were also very simply and usually boasted a central fire for warmth. Thatch was frequently used for the roofs and these homes seldom had windows at all.
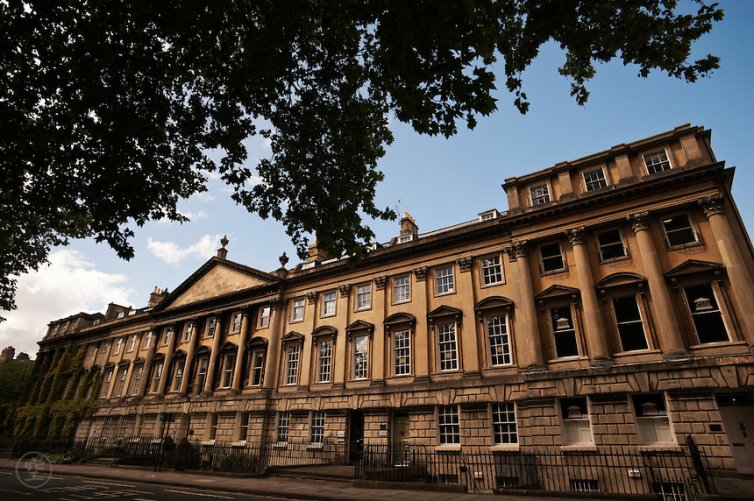
Elizabethan
By the second half of the 16th century, the country was almost bankrupt, thanks to Henry VIII. However, when Queen Elizabeth took over the throne, it began an economic revival, based especially on agriculture and farming. This led to the building of a number of small houses as well as huge mansions situated out in the English countryside. Older styles were modernised and new buildings reflected the Elizabethan trends of a very symmetrical layout in an E shape, with exquisite formal gardens. Some of these homes also displayed somewhat of a Dutch influence, with curved gables as a noteworthy example. A long gallery was another major characteristic of this era, and was used for displaying portraits or for family get-togethers. This gallery would have several fireplaces along one wall and windows along the other three.
The entrance hall was grand and elaborate, granted the most attention and intended to impress guests and testify to one.s wealth.
Most Elizabethan houses were made from stone, while some were made from a combination of stone and wood. Elaborate embellishments were created using moulded plaster. This was known as strapwork.